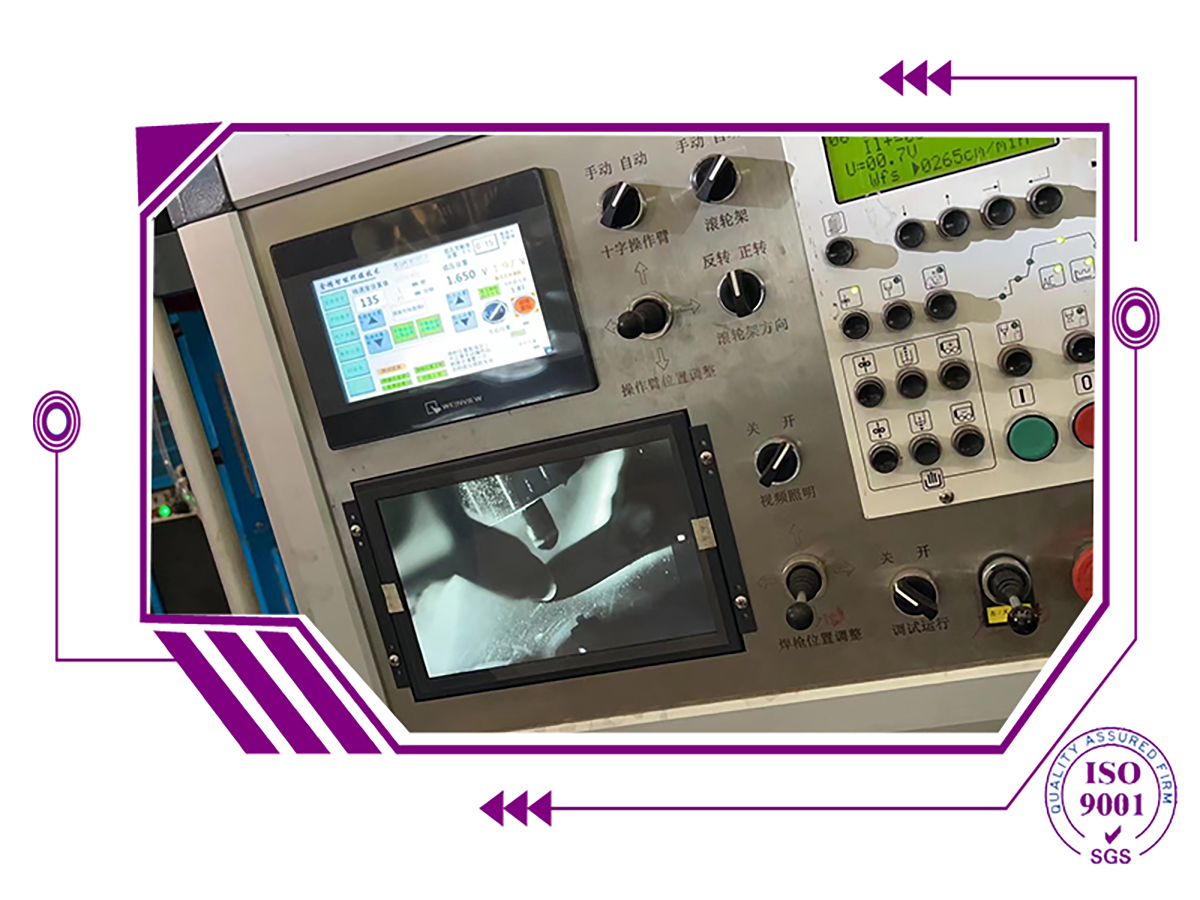
Welding Camera Apply in TIG Plasma Welding and LCD Camera Monitor for Welding Line Dynamic Range Image + 140 dB, The Ds30 Can Acquire Images with a Great
High Dynamic Range (HDR)
With a dynamic range image + 140 dB, the DS30 can acquire images with a greater range of tonal detail than any standard camera.
This is particularly important for welding processes where there is a very bright light source in the image that needs to be seen in great detail as well as the darker surrounding background features.
Color When You Need It
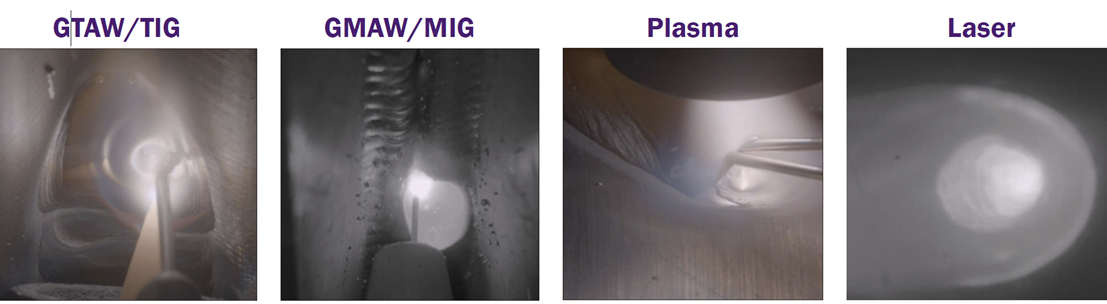
With HDR color imaging, the DS30can acquire color images for various welding processes, such as GTAW, where color provides extra information such as: the boundary of the Heat Affected Zone, oxidation of the melt pool and tip, and shielding gas presence. The very bright weld arc can be seen in color without saturation as well as its darker surround- ing background features.
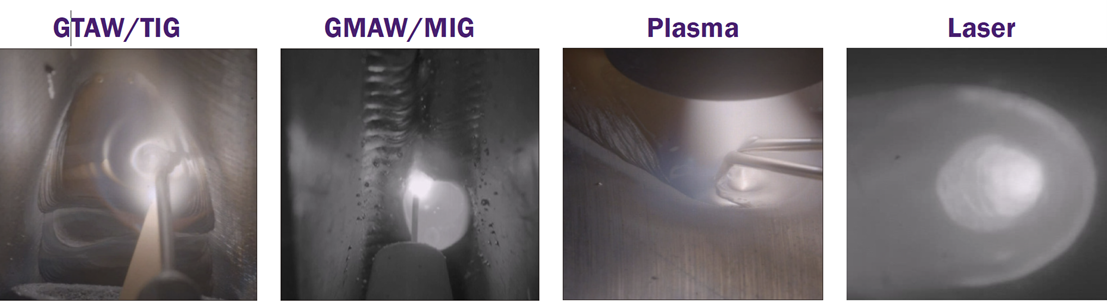


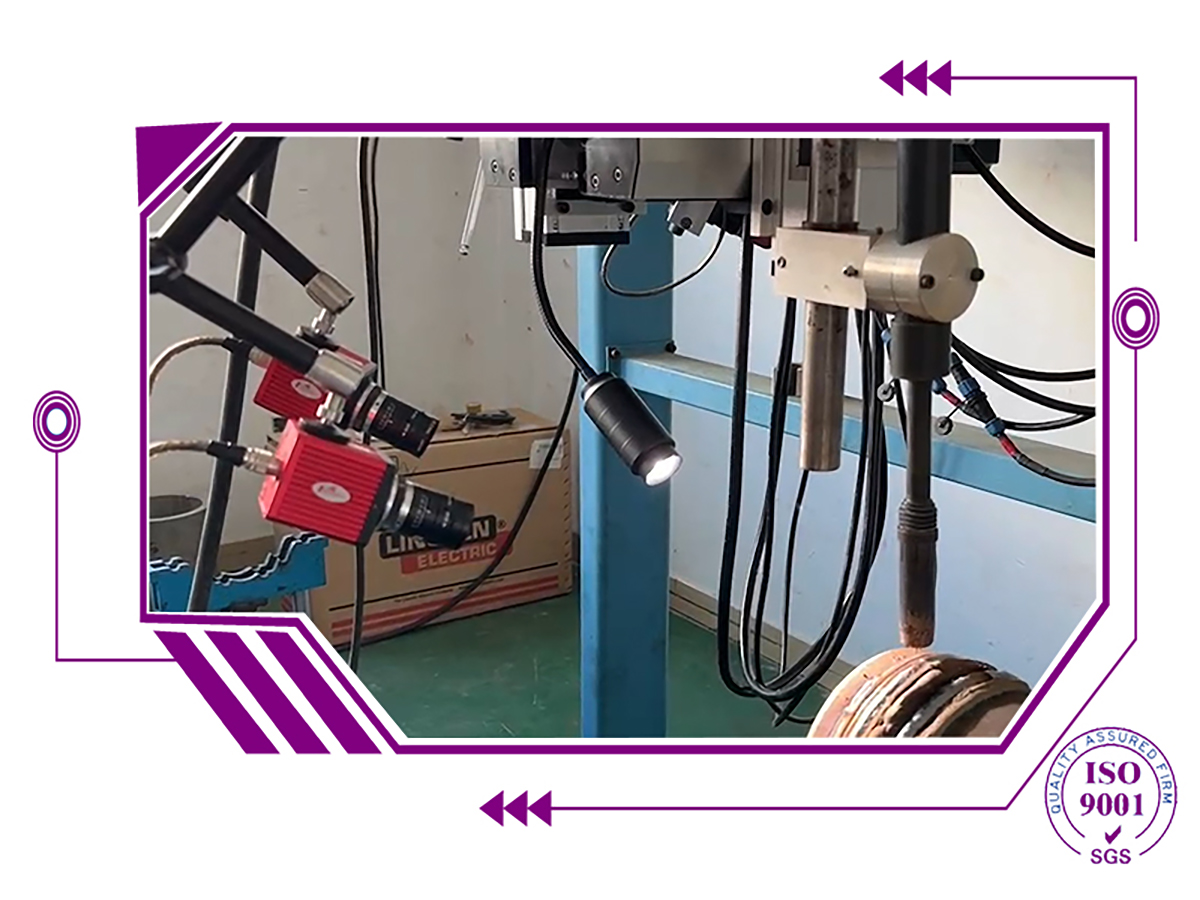
Welding cameras traditionally have been employed to aid automated or mechanized welding of inaccessible joints and ensure the integrity of critical welds.
Cameras are practical tools for many other welding applications, too, now that recent advances in electronics have enhanced the image quality and reduced the price of such equipment.
Welding cameras are particularly useful for improving working conditions, weld quality, set-up speed, positioning accuracy, and facilitating quality assurance.
++ Welding Cameras Use In Automated Welding Procedures
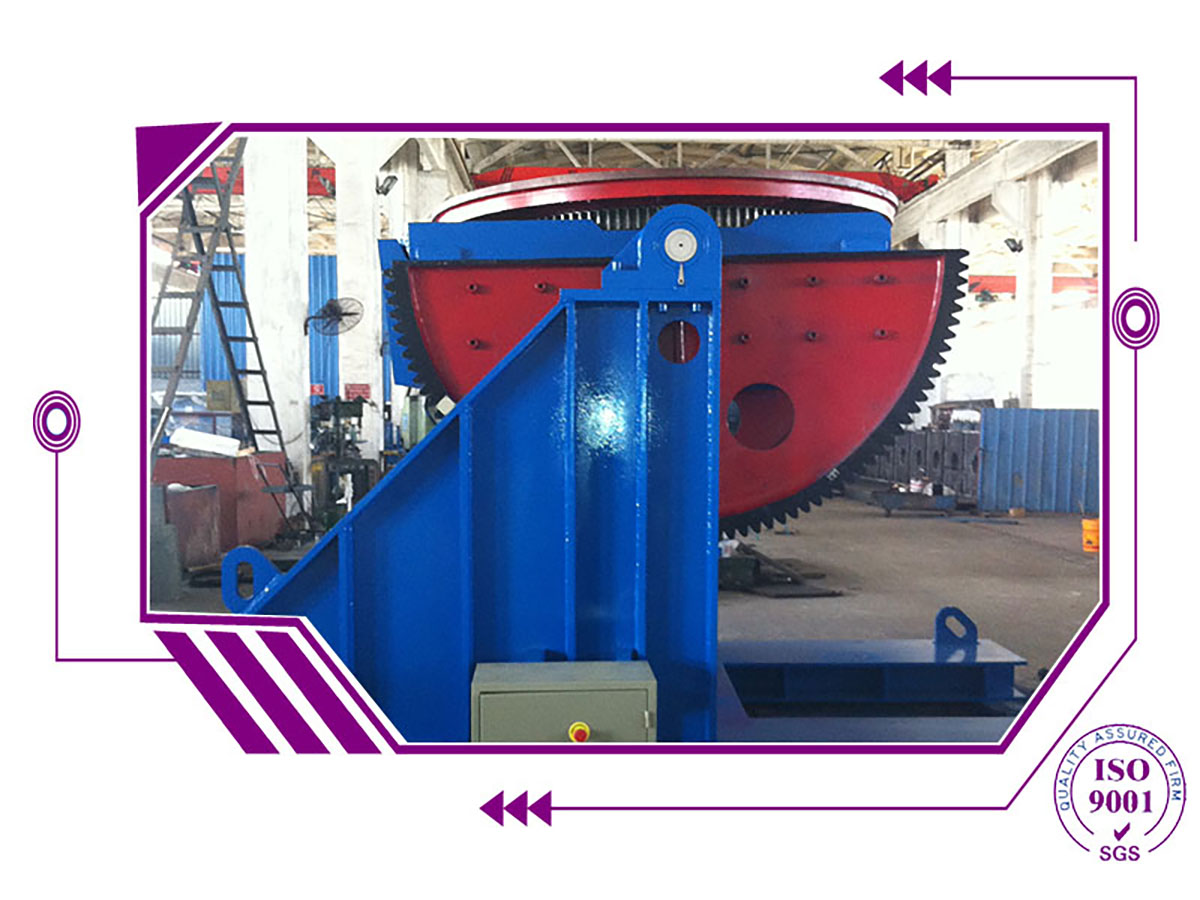
From job-shop manual welding to push-button automated welding, fabricators employ a wide range of automation techniques to improve productivity and weld quality, as well as to ensure a welder's health and safety. Relatively simple circumferential and linear joint-seams are often welded using positioners, rotators, column and booms, seamers, lathes, tractors, orbital welders, etc. Such equipment may use sensors to automatically control the process (automated welding), or the operator may manually control the movement and/or torch (mechanized welding).
In either case, a clear view of the weld pool can significantly benefit the welding operation.
++ Applications and Benefits of Cameras in Automated Welding
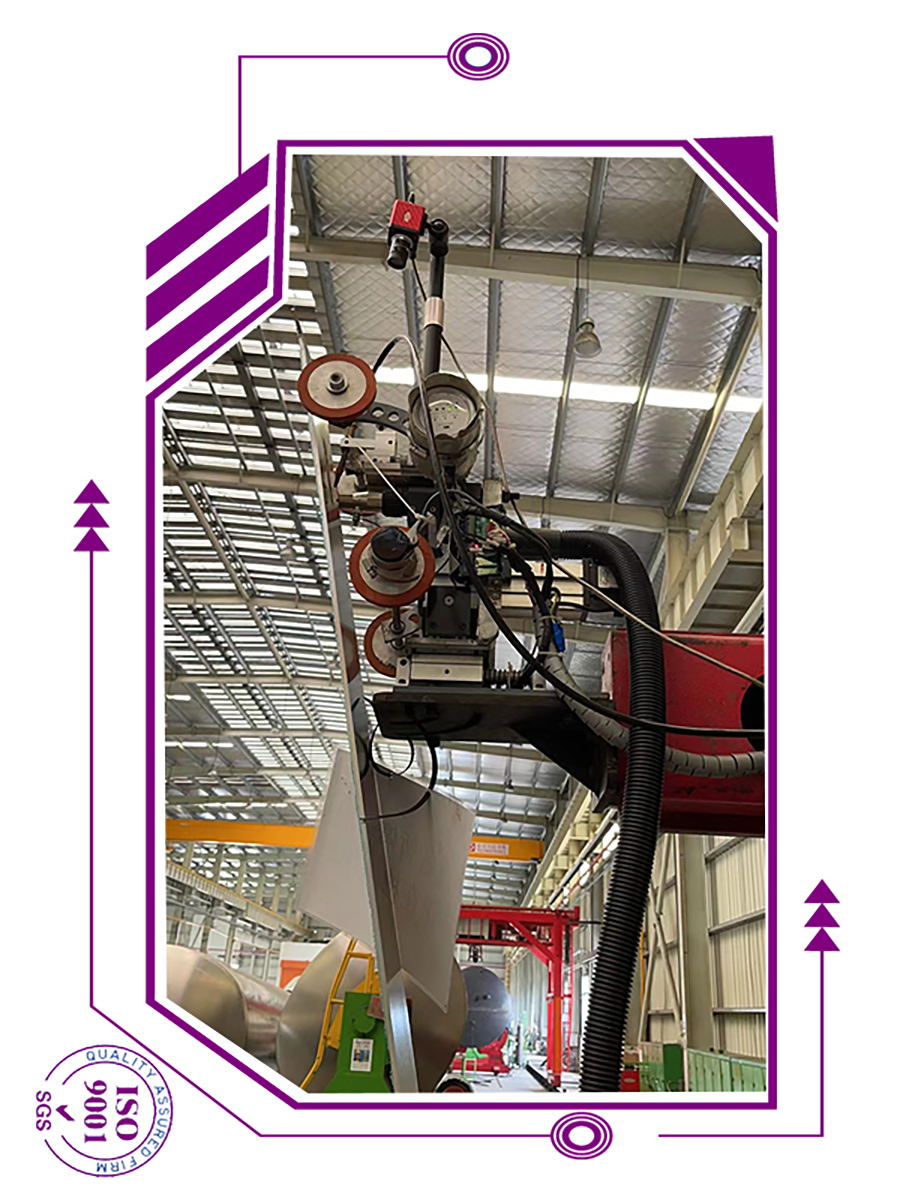
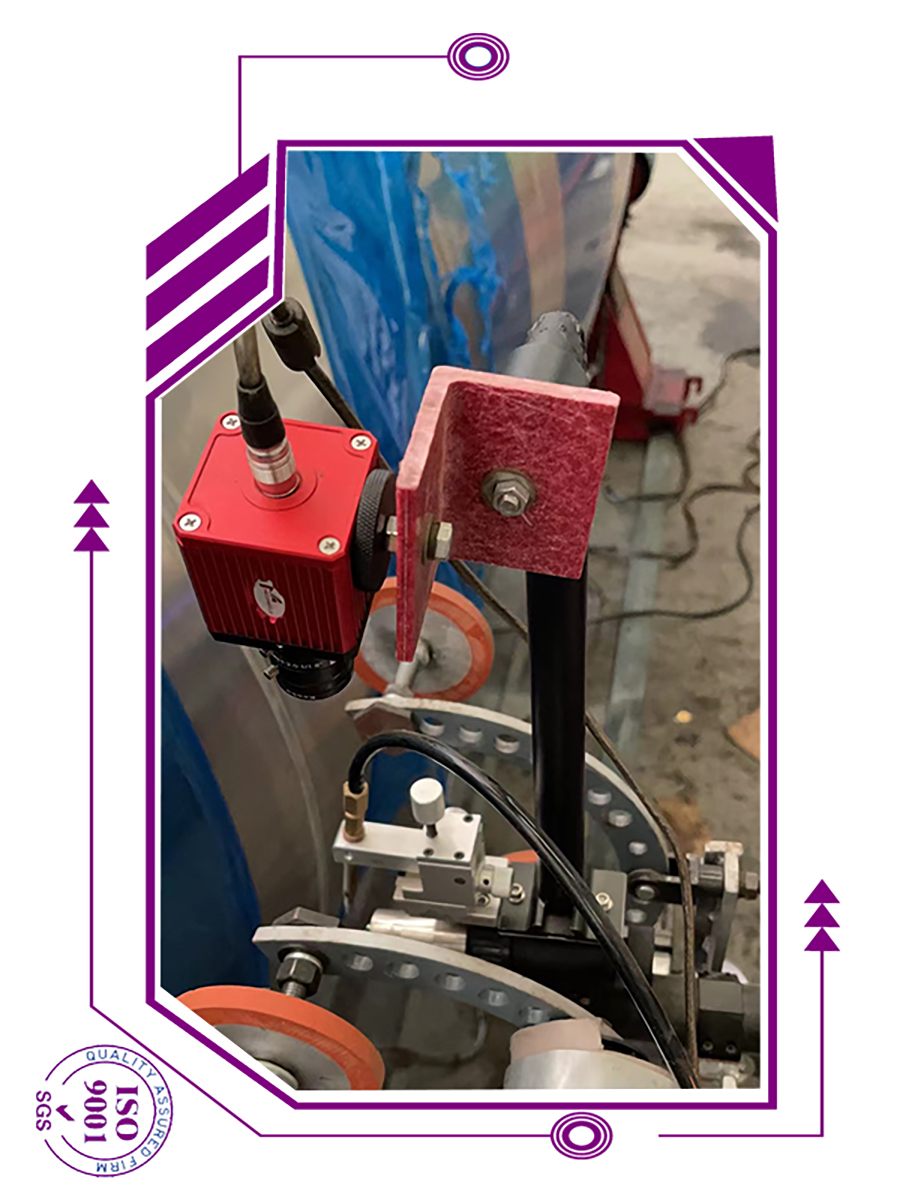
The use of camera systems in automated welding arose from necessity. Welding in hazardous environments subject to nuclear radiation, vacuums, lasers, argon, or water entails the use of welding cameras to control the torch head remotely and wire feed positions as well as to monitor the welding process. Welding cameras provide similar benefits in automated applications with restricted access (including bore cladding, orbital welding, and welding at height) or joints subject to preheating
++ Weld Quality Inspection In Real Time
In addition to positioning the torch before and during welding, cameras may be used as a real-time post-weld inspection tool by positioning the camera for views of the solidifying weld pool.In many cases, welding cameras are applied to monitor the welding of critical joints or expensive materials. For these applications, the cost of failure is significant, and the ability to take pre-emptive action is essential.
++ Improving Welding Speed And Accuracy
However, welding cameras are no longer restricted to the most sensitive and expensive welding operations. Advances in camera electronics have improved image quality and reduced purchase costs, such that welding cameras now prove beneficial to many more automated welding applications. For example, a magnified view of the electrode and torch helps improve the set-up speed and accuracy of automated micro TIG and PAW, dabber TIG, and tube mill applications. The performance of mechanical joint tracking systems is enhanced by camera supervision. Cameras applied to carriages facilitate welding upside down, at height, inside confined spaces, and around circumferential joints.
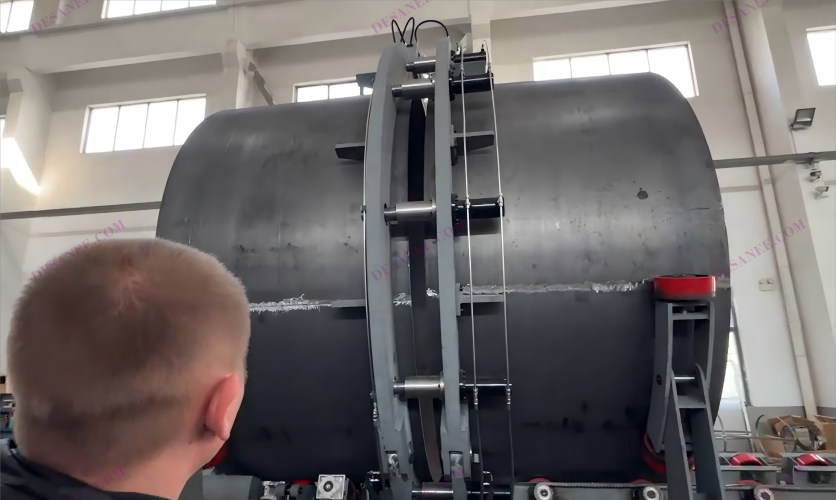
Automated systems with multiple weld-torches, like those used to manufacture turbine shafts, welded I-beams, spiral tubes, and tanks, may be effectively monitored and controlled from a single console.